1. What is a contactor?
Contactor (also known as contactor) is a low-voltage electrical device, often used to perform switching of power circuits, especially in applications requiring switching of large currents. It is also known as a starter , an important device in the electrical control system.
Contactor is a very popular electrical device in automation and control systems. Some common applications using Contactor are motor control, capacitor bank, lighting system, etc.
The switching operations of contactors can be performed through different mechanisms, including electromagnetic, pneumatic, or hydraulic mechanisms. However, in this article, we will focus only on electromagnetic contactors – the most common type of contactor.

2. Structure of Contactor
Contactor consists of 3 main parts:
a. Electromagnet
+ Coil : Creates magnetic force when electric current runs through.
+ Iron core : This magnetic core moves when there is suction from the coil.
+ Spring : Helps push the lid back to its original position when the coil is not powered.
b. Arc extinguishing system
When switching on and off an electrical circuit, an electric arc can form, causing wear and damage to the contacts. The arc extinguishing system has the role of limiting and eliminating this phenomenon, protecting the contacts from burning.
c. Contact system
Contactors consist of two main types of contacts:
+ Main contact: Capable of transmitting large currents. This contact is usually a normally open (NO) contact and only closes when the circuit is powered.
+ Auxiliary contacts: These are smaller contacts, with a maximum current of about 5A. Auxiliary contacts can be in the normally closed (NC) or normally open (NO) state, and are responsible for controlling small circuits in the system.
Normally closed contact is a type of contact that is in the closed state (there is communication between the two contacts) when the magnet coil in the contactor is in the idle state (not supplied with electricity). This contact opens when the contactor is in the active state. The opposite is the normally open contact.
Main contacts are typically used in power circuits (e.g. motor control), while auxiliary contacts are typically used in control circuits.
3. Operating principle
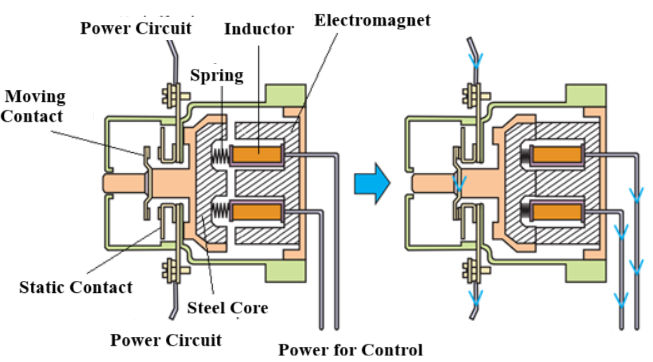
When voltage is applied to the contactor coil (usually 220V AC or 380V AC), the coil will generate magnetic force, attract the movable iron core and form a closed magnetic circuit. At this time, the magnetic force will overcome the spring reaction force, causing the contactor to switch to the operating state.
When the contactor is operating:
♦ The main contact closes, completing the electrical circuit that supplies power to the device.
♦ The auxiliary contact switches to its state, which can be open or closed depending on the requirements of the control circuit.
When the power supply to the coil is stopped, the contactor will return to its resting state, and the contacts will open or close again as in the original state.
4. Basic parameters
+ Rated current: Maximum current that the contactor can transmit without overheating.
+ Rated voltage: Is the operating voltage on the coil and circuit.
+ Closing capacity: Is the ability to close the circuit. This value is usually from 1 to 7 times the rated current.
+ Breaking capacity: Is the ability of the contactor to break the circuit when there is a large current. Usually from 1 to 10 times the rated current.
+ Mechanical durability: Is the number of on/off times that the contactor can perform without causing damage, usually from 5 million to 10 million on/off times.
+ Electrical durability: Is the number of times the contactor can open and close the rated current without being damaged. Usually ranges from 200,000 to 1 million times.
What are the advantages of Contactor (CTT)?
♦ Compact size : CTT has a small design, helping to save installation space, especially useful in electrical systems with limited space.
♦ Remote control : CTT allows to open and close the circuit remotely through controllers such as push buttons, PLC, or automatic control.
♦ High safety : The contactor’s protective cover prevents arc discharge, ensuring safety for operators and equipment.
♦ High durability : CTT has high durability, fast switching time and stable operation.
Thanks to these advantages, contactors are widely used in circuit switching control applications in industrial plants and automation systems.
What is the application of Contactor (CTT)?
It have many applications in automation and control, including:
+ Motor control : CTT can supply power to start motor directly or combine with thermal relay to protect motor from overload.
+ Star-delta starting : CTT is used in star-delta starting diagram to reduce motor starting current.
+ Capacitor control : CTT helps to close and open capacitors in the circuit to compensate for reactive power.
+ Lighting system control : Can combine CTT with PLC or time relay to turn on and off lighting automatically.
+ Phase protection : CTT combined with phase protection relay to protect equipment from problems such as phase loss, phase deviation, overvoltage, undervoltage, etc.
5. How to choose the right Contactor
Selecting contactor for motor:
To choose the right Contactor for the motor, we must rely on basic parameters such as ${{\rm{U}}_{{\rm{rated}}}}$, P, ${\rm{Cos}}\varphi $
– ${{\rm{I}}_{{\rm{rated}}}}$ = ${{\rm{I}}_{cal}}$ x 2
– ${{\rm{I}}_{ct}}$= (1.2 – 1.5) x ${{\rm{I}}_{{\rm{rated}}}}$
Apply to a specific example below :
Load 3P, 380V, 3KW motor, calculate rated current according to the following formula:
${{\rm{I}}_{{\rm{rated}}}}$ = P / (1.73 x 380 x 0.85) where the cosphi coefficient is 0.85.
We calculate: ${{\rm{I}}_{{\rm{rated}}}}$ = 3000 / (1.73 x 380 x 0.85) = 5.4 A
${{\rm{I}}_{ct}}$ = (1.2 – 1.4) ${{\rm{I}}_{{\rm{rated}}}}$ .
We calculate: ${{\rm{I}}_{ct}}$ = 1.4 x 5.4 = 7.56A
Should choose 3 phase Contactor with current larger than calculated current.
You can choose LS 3-phase (MC-9b), Mitsubishi (S-T10), Schneider (LC1D09),…
When selecting for a motor, attention must be paid to the coil voltage and auxiliary contacts.
Selecting for capacitor bank
To choose the right Contactor for the capacitor, we must rely on the rated current of the capacitor.
For example, a 3-phase 415V 50kVAr capacitor has a rated current of 69.6A.
Choose a CTT larger than 1.2 times the rated current of the capacitor = 6.9.6A x 1.2 = 83.52A.
You can choose LS 3-phase 85A contactor (MC-85a), Mitsubishi 3-phase 100A contactor (S-T100),…
Choosing high current contactor is better but the cost will be higher, larger size will take up more installation space.
In addition, the coil voltage must be noted. Contactors used for capacitors can use 2 types of coils: 220VAC or 380VAC. The most commonly used type of Contactor is the 220VAC coil.
Conclude
Contactor is an important device in electrical automation and control, helping to open and close the circuit accurately and safely. Understanding the structure, operating principles and applications of contactor will help you apply it effectively in electrical and automation systems.
Hope this article helps you master the knowledge of what a Contactor is and apply it successfully in work and study.
Total Readers: 644